Testosterone, often dubbed the “male hormone,” plays a crucial role in men’s health and vitality. However, various factors can contribute to decreased testosterone levels, leading to a range of symptoms and health concerns. Understanding the common causes of low testosterone is essential for identifying potential issues and seeking appropriate interventions. In this article, we’ll delve into some prevalent culprits behind low testosterone levels in men and explore how addressing these factors can help restore hormonal balance and optimize overall well-being.
Age-related Decline:
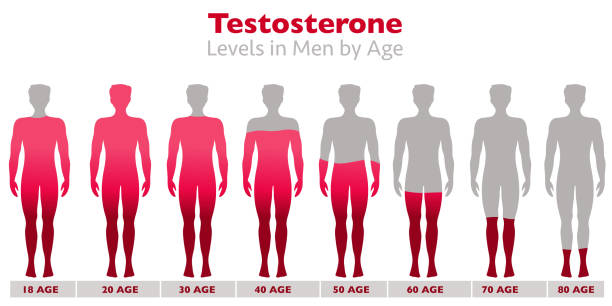
As men age, it’s natural for testosterone levels to gradually decrease. This decline typically begins around the age of 30 and continues at a rate of about 1% per year. While aging itself isn’t a cause for alarm, declining testosterone levels can lead to various symptoms, including decreased energy, reduced muscle mass, and diminished sexual function.
Lifestyle Factors:
Several lifestyle factors can contribute to low testosterone levels. These include:
Poor Diet: Diets high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact hormone levels. Opting for a balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and essential nutrients can support hormonal health.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise and physical activity can contribute to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, all of which are associated with lower testosterone levels. Regular exercise, including both cardiovascular and strength training, can help boost testosterone production and improve overall health.
Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress can disrupt hormone balance and suppress testosterone production. Finding effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or relaxation exercises, can
help mitigate these effects and support hormonal health.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can interfere with the body’s ability to produce or utilize testosterone effectively. These include:
Hypogonadism: A condition characterized by inadequate testosterone production in the testes. Hypogonadism can be caused by genetic factors, autoimmune diseases, infections, or damage to the testes.
Obesity: Excess body fat, especially abdominal fat, is associated with lower testosterone levels and increased estrogen production. Addressing obesity through diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications can help
improve hormonal balance.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to insulin resistance, which in turn can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to low testosterone. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and
medication can help mitigate these effects.
Medications and Substance Abuse:
Certain medications and substances can interfere with testosterone production or metabolism. These include:
Opioids: Long-term use of opioid medications can suppress testosterone production and lead to hormonal imbalances.
Corticosteroids: Prolonged use of corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, can inhibit testosterone production and increase the risk of hypogonadism.
Alcohol and Drug Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption and substance abuse can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to low testosterone levels. Seeking treatment for addiction and adopting healthier lifestyle
choices can support hormonal health.
Low testosterone levels can have far-reaching implications for men’s health and well-being. By addressing common underlying causes such as aging, lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and medication use, individuals
can take proactive steps to optimize testosterone levels and improve overall health. If you’re experiencing symptoms of low testosterone or have concerns about your hormonal health, consult with a qualified healthcare provider for personalized evaluation and treatment recommendations. Taking proactive steps to address low testosterone can help you reclaim vitality and enhance your quality of life.
See what KP has to say about it: https://www.instagram.com/p/C1-hZjlJjqo/
